Preclinical Echocardiography for Cardiology Research
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) ultrasound provides superior resolution and will have an incredible impact on cardiovascular research in your animal models.
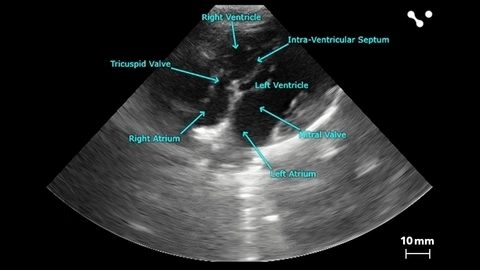
Perform reliable echocardiography in any animal model for translational cardiovascular research with in vivo resolution down to 30 microns.
Vevo ultrasound imaging platforms provide the best temporal and spatial resolution compared to MRI, conventional ultrasound and CT. The Vevo F2 system can perform preclinical echocardiography in animal models all the way from zebra fish and mice to pigs. Vevo technology has been established as a gold standard technology for mouse cardiac imaging, having been utilized in over 3,000 peer-reviewed publications.
With the Vevo imaging systems you can:
- Perform cardiovascular phenotyping for cardiac structure and function, ideal for stress echo and cardiotoxicity studies
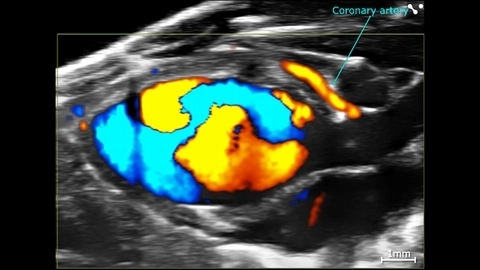
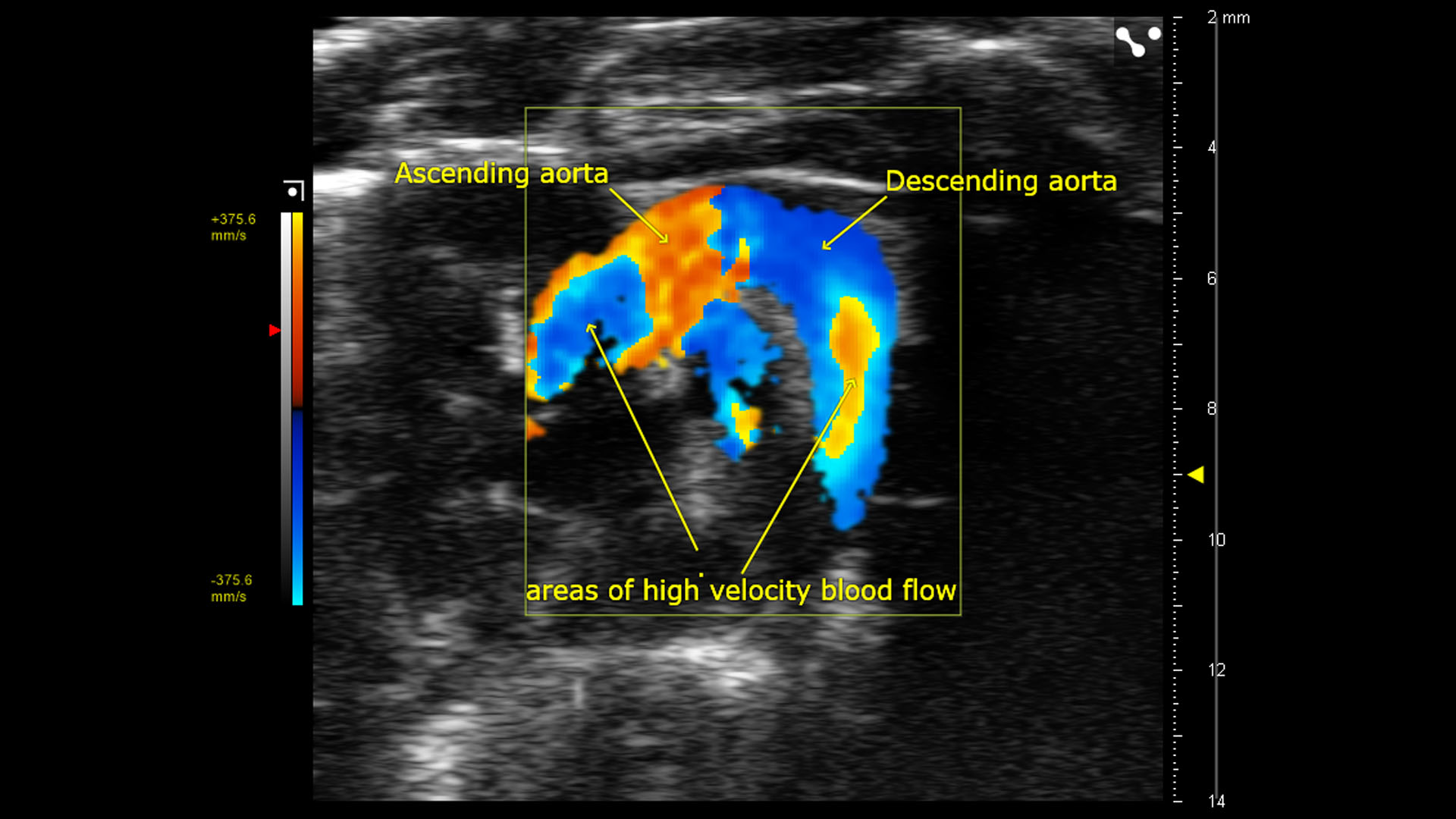
- Image the heart in 4D (with Color or Power Doppler integration)
- Quantify diastolic dysfunction
- Evaluate early signs of cardiac dysfunction with cardiac strain (global or regional synchrony and deformation)
- Perform image-guided cardiac injections
- Monitor full animal physiology while imaging, including body temperature, ECG and respiratory rate
- Assess myocardial oxygen saturation
Cardiac 4D Imaging
Quantify ejection fraction and fractional shortening with more accuracy than traditional echocardiography, and faster than cardiac MRI!
The Heart of the Matter
If you missed this advanced workshop on COVID-19 and other preclinical cardiac disease models, here's your chance to catch up.